GCP 101: Google Cloud Storage
Google Cloud Storage was publicly launched in 2010 as a competitor to other cloud-based storage services such as Amazon S3.

Introduction
Cloud storage has revolutionized the way businesses manage data. Among the plethora of available services, Google Cloud Storage (GCS) stands out for its flexibility, scalability, and robustness. As part of Google Cloud's vast ecosystem, GCS provides a unified object storage solution, facilitating the storing, retrieving, and managing of data on a massive scale for millions of businesses worldwide.
Origin of Google Cloud Storage
Google Cloud Storage was publicly launched in 2010 as a competitor to other cloud-based storage services such as Amazon S3. Built on Google's innovative and highly efficient infrastructure, GCS has continually evolved, introducing new features and improvements over the years.
In its inception, GCS was primarily designed to manage unstructured data such as videos, pictures, and logs. Over time, however, Google expanded its functionalities, making it more versatile for a broader spectrum of applications. Now, it caters to diverse use cases ranging from disaster recovery to content delivery networks (CDN), web and mobile applications, and data archiving.
Benefits of Google Cloud Storage over On-premises Servers
Shifting from on-premises servers to Google Cloud Storage can bring a multitude of advantages to businesses:
- Cost-effectiveness: Managing on-premises servers incurs costs for hardware, maintenance, and IT personnel. GCS, with its pay-as-you-go model, can significantly reduce these costs. Additionally, with the various storage classes offered by GCS, you can choose the option that best fits your budget and usage patterns.
- Scalability: GCS provides virtually unlimited storage capacity, which can be increased or decreased as needed, eliminating the need for upfront storage allocation. This flexibility allows businesses to adapt quickly to changes in data storage requirements.
- Data Protection and Security: GCS leverages Google's advanced security model, which includes data encryption at rest and in transit, identity and access management controls, and robust auditing and logging features. This ensures your data is secure and protected against threats.
- Global Access and Collaboration: As a cloud-based solution, GCS allows data to be accessed from anywhere in the world. This facilitates collaboration among teams distributed across different locations.
Architecture of Google Cloud Storage
GCS's architecture is designed around the concept of objects and buckets. Objects refer to the files stored in GCS, while buckets act as containers for these objects, somewhat akin to a directory in a traditional file system.
Each object stored in GCS is associated with metadata containing information such as the object's size, the last modification time, and media type. Additionally, objects are assigned a unique key by which they can be retrieved.
The buckets in GCS are globally unique and designed to be highly scalable. Each bucket is associated with storage classes (Multi-Regional, Regional, Nearline, and Coldline), which determines its availability and pricing.
The architecture of GCS also allows for the fine-tuning of access controls and permissions at both the bucket and object level. This flexibility, combined with the security and encryption measures in place, ensures the secure storage and retrieval of data.
Bucket Types in Google Cloud Storage
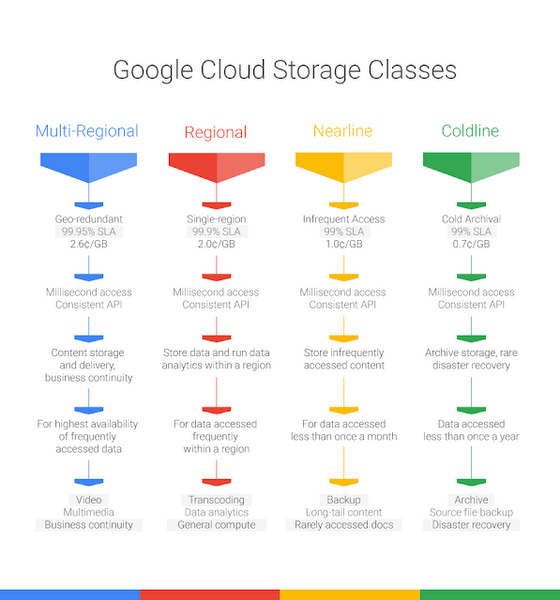
There are four types of storage classes or buckets available in GCS, each designed for specific use cases:
- Multi-Regional Storage: This class is designed for storing frequently accessed data that needs to be geographically distributed, such as data for websites, streaming and gaming content. It offers the highest level of availability and redundancy.
- Regional Storage: Ideal for storing data that is frequently accessed within the same region, such as data used in compute instances. It is often used for analytics, and machine learning workloads.
- Nearline Storage: This is a low-cost, highly durable storage service for storing infrequently accessed data. It is ideal for data you expect to read or modify approximately once a month, like backups and older content that needs to be available quickly.
- Coldline Storage: The most economical option, Coldline storage is designed for data that is accessed less than once a year. It's ideal for long-term archiving and disaster recovery.
Choosing the right bucket type is crucial as it directly impacts the cost, performance, and availability of your data.
| Bucket Type | Ideal For | Data Availability | Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| Multi-Regional | Frequently accessed data that needs high availability and geographical distribution. Examples include data for websites, streaming, and gaming content | High (Designed for 99.95% availability) | Highest cost per GB |
| Regional | Frequently accessed data within the same region, such as data used in compute instances, analytics, and machine learning workloads | High (Designed for 99.9% availability within a single region) | Lower cost per GB compared to Multi-Regional |
| Nearline | Infrequently accessed data, such as backups and older content. Ideal for data you expect to access approximately once a month | Lower (Designed for 99% availability) | Lower cost per GB compared to Regional but retrieval costs apply |
| Coldline | Data accessed less than once a year, such as long-term archiving and disaster recovery | Lowest (Designed for 99% availability) | Lowest cost per GB but retrieval costs apply |
Features of Google Cloud Storage
Google Cloud Storage offers a wealth of features designed to provide a robust and flexible storage solution:
- Object Lifecycle Management: This feature allows you to automatically move objects between different storage classes based on their age or other conditions, helping manage costs effectively.
- Consistency: GCS provides strong read-after-write consistency, which means that once data is written, any subsequent access will return the most recent write.
- Versioning: GCS allows you to preserve, retrieve, and restore every version of every object in your bucket, providing protection against inadvertent overwrites and deletions.
- Data Transfer: GCS provides various options to transfer your data into Google Cloud, including online transfer services, transfer appliances for offline data ingestion, and gsutil, a command-line tool for interacting with GCS.
One of the killer features of GCS is its integration with other Google Cloud services, providing a seamless and efficient way to build, deploy, and scale applications.
Comparison with Other Cloud Storage Solutions
Google Cloud Storage, AWS S3, and Azure Blob Storage are three major players in the cloud storage market. Each has its strengths and unique features:
- AWS S3: Amazon S3 is known for its durability and robust ecosystem. It provides a wide range of storage classes similar to GCS, from frequently accessed data to long-term archiving (Glacier). However, unlike GCS, S3 uses a region-based namespace, meaning the bucket names are not globally unique.
- Azure Blob Storage: Microsoft's Azure Blob Storage also offers a suite of features, including tiered storage options (Hot, Cool, and Archive). Azure often stands out for its seamless integration with other Azure services and Microsoft's enterprise-focused tools and software.
While GCS, S3, and Azure offer similar core functionalities, the choice often depends on the specific requirements of the project and the ecosystem you are invested in or prefer.

Best Practices for Using Google Cloud Storage
Here are some recommendations to make the most of Google Cloud Storage:
- Data Organization: Plan your bucket structure effectively considering your data retrieval patterns. Keep in mind that operations in GCS are atomic at the object level.
- Security Measures: Use Identity and Access Management (IAM) roles and policies to regulate access to your buckets and objects. Enable Object Versioning to safeguard against accidental data loss.
- Optimal Use of Storage Classes and Lifecycle Policies: Take advantage of the different storage classes based on your data access patterns to optimize costs. Implement lifecycle policies to automate data management.
- Cost Management: Monitor your storage usage with Google Cloud's operations suite and use the Google Cloud Pricing Calculator to estimate costs.
Case Studies of Google Cloud Storage Implementation
Several businesses have leveraged GCS to transform their data management. For example, Spotify migrated all of its data storage and computation from its own servers to Google Cloud, including GCS. This move enabled them to focus more on providing value to their customers instead of maintaining hardware.
Another example is Twitter, which uses GCS for storing and analyzing the vast amount of data generated by its users. With GCS, Twitter has been able to process data at a scale that was not possible with their previous solution.
Future Trends and Developments in Cloud Storage
The cloud storage market continues to evolve with the changing landscape of digital needs. Here are a few trends to watch out for:
- Multi-cloud Strategies: As businesses seek to avoid vendor lock-in and improve system resilience, a trend towards multi-cloud strategies is emerging, where data and applications span across multiple cloud providers.
- Increased Importance of Security: With the rise in cyber threats, the focus on data security in cloud storage is more critical than ever. Expect developments in encryption technologies, access control mechanisms, and more.
- AI and Machine Learning: Integrating AI and machine learning with cloud storage can facilitate more intelligent data management, predictive analytics, and enhanced data governance.
Given Google's innovation prowess, we can expect GCS to continue evolving, aligning with these trends, and meeting the ever-growing data needs of businesses.
About 8grams
We are a small DevOps Consulting Firm that has a mission to empower businesses with modern DevOps practices and technologies, enabling them to achieve digital transformation, improve efficiency, and drive growth.
Ready to transform your IT Operations and Software Development processes? Let's join forces and create innovative solutions that drive your business forward.
Subscribe to our newsletter for cutting-edge DevOps practices, tips, and insights delivered straight to your inbox!
